Action Plan Summary
Pandemics sicken and kill people in three ways:
first by overwhelming patients’ immune defenses, then by swamping hospital networks, and eventually by cutting off a community’s economic lifeblood. Hence, “saving lives or saving the economy” is a false choice. As of April 19, Covid-19 had directly killed more than 163,000 people worldwide, including nearly 35,000 in the United States. But the indirect effects are still being counted. The Great Recession of 2008, for instance, killed people in the thousands by disrupting healthcare for mothers, children and those with chronic illnesses and increasing a host of deadly mental and social conditions like alcoholism, depression and domestic abuse.
With the first wave of infections from the Covid-19 pandemic cresting in much of the country, American political and business leaders rightly are considering plans to reopen the economy. This Action Plan is intended to serve as a resource guide for that all-important project.
The bad news is that the U.S. is not yet administering enough coronavirus tests each week to adequately monitor the entire U.S. workforce or rapidly detect recurrent Covid-19 outbreaks. Such outbreaks can be expected for the foreseeable future given the low level of population immunity as well as the virus’s contagiousness and wide geographic dispersion. The location and size of recurrent outbreaks are difficult to predict. Close monitoring of the medically vulnerable, institutionalized, poor and imprisoned is vital.
The good news is that in the coming weeks the country could have the tools needed to allow governors and other officials to lift the most severe lockdowns and begin a phased reopening of some businesses. The goal is to allow enough economic activity to forestall a full-blown depression while keeping Covid-19 infection rates low enough to prevent hospitals from being overwhelmed and thereby causing a wider and more deadly health crisis.
This will be a delicate balancing act. Adjustment inevitably will need to be made based on close monitoring of the pandemic. Reopening the economy will be most successful if we move decisively to both increase testing capacity and optimally deploy testing supplies.
The goal of the Action Plan is to build a state-led national program of Covid-19 testing that supports reopening the economy through the goals of workforce monitoring, early detection of recurrent outbreaks, and diagnostic and home testing.
This would be the largest public health testing program in American history. Success will depend on the active engagement of the government, business, philanthropy, and the public.
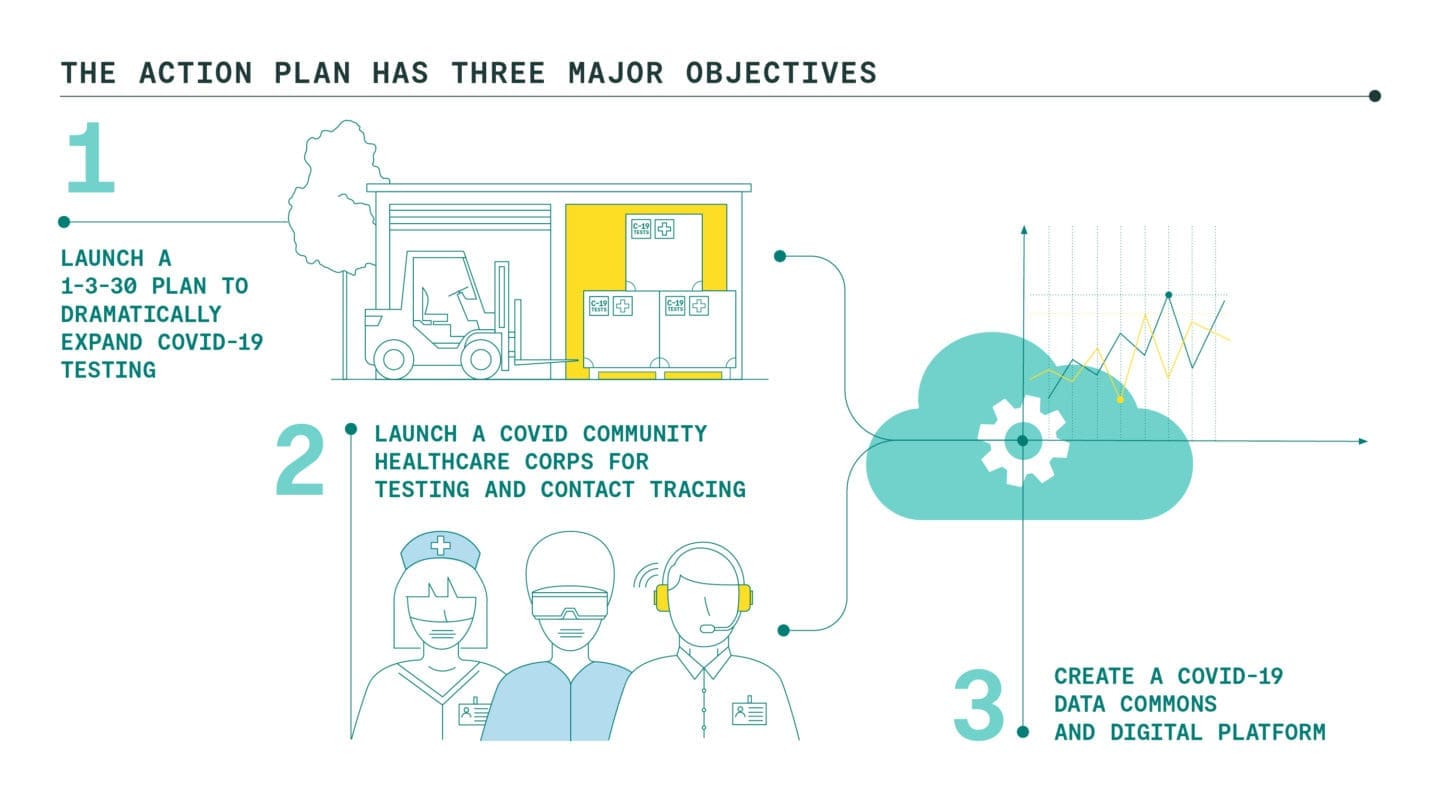
Launch a 1-3-30 Plan to Dramatically Expand Covid-19 Testing
We are proposing our nation come together around the bold, ambitious, but achievable goal of rapidly expanding testing capacity to 30 million tests per week over the next six months. This 1-3-30 Plan would be achieved by: (1) creating an Emergency Network for Covid-19 Testing to coordinate and underwrite the testing market, (2) launching an eight-week National Testing Laboratory Optimization Initiative to increase output to 3 million tests per week from the current one million, and (3) investing in a Testing Technology Accelerator to further grow U.S. testing capacity from 3 million to 30 million tests per week.
The steady increase in U.S. testing that began in late February has now plateaued. During the first two weeks of April, the number of tests per day averaged 143,000 (~ 1 million tests per week) with no appreciable upward trend.[i] As of April 18, 2020, the U.S. had completed 3,698,534 tests of which 722,182 were positive (19.50%)
This undoubtedly reflects just the tip of the COVID-19 pandemic in the U.S. Current barriers to rapid increases in American test production, supply, distribution and administration include uncertainty over financing and payment; lack of coordination of local, state, and national purchases; uneven distribution of test kits; severe shortages of reagents; regulatory barriers; and a severe lack of staffing.
The 1-3-30 Plan aims to overcome these barriers and progressively expand testing from the current one million to three million and then to 30 million tests per week through three action steps.
ACTION STEPS:

To drive rapid scale-up of Covid-19 testing, the ENCT will engage with: producers of testing equipment, reagents, and other lab consumables; national, state and local purchasers; public and private healthcare funders; and financial institutions. The ENCT will also work to identify and resolve choke points in the test supply chain. The ENCT should convene a consensus group of national, state, business, and academic leaders on the use of testing for workplace monitoring and early detection of Covid recurrences. An overarching analysis of the testing supply chain both in the United States and globally should be undertaken immediately.

This will be achieved by unleashing the untapped potential of existing test capacity at national, university, and local labs. Importantly, this program would bolster the capacities and resources of thousands of small laboratories around the country. Supply constraints will be identified and eliminated.

This increase will depend on realizing and rolling out the best mix of new technologies for higher efficiency laboratory testing, point-of-care office testing, and home-testing. In addition, some of this increase can be achieved through process efficiencies and lab techniques such as batch sampling. The powers of the Defense Production Act may will be need to be invoked given the inherent commercial uncertainties in this 10-fold production increase.
Launch a Covid Community Healthcare Corps for testing and contact tracing
The taking and preparation of samples, analysis of testing, and human-centered privacy-protected contact tracing will require a massive amount of manpower that can be stood up in the next few weeks by federal, state, and local hiring authorities with funding offered via block grants to states.
The number of tests needed to successfully prevent recurrent outbreaks while allowing some relaxation of social distancing will depend on the vigilance of contact tracing. With the kind of high-precision contact tracing used in South Korea, just 2.5 to 5 million tests per day would be required. With the imprecise tracing of a country like Taiwan, 30 million tests per day would be needed – a level far beyond present capacities.
ACTION STEPS:
 At least 100,000 people and perhaps as many as 300,000 must be hired to undertake a vigorous campaign of test administration and contact tracing, and they must be supported by computer systems networked with regional and national viral datasets and as many electronic health records from local hospital systems as can be provided. The CCHC should designate staff to distribute, administer and oversee testing.
At least 100,000 people and perhaps as many as 300,000 must be hired to undertake a vigorous campaign of test administration and contact tracing, and they must be supported by computer systems networked with regional and national viral datasets and as many electronic health records from local hospital systems as can be provided. The CCHC should designate staff to distribute, administer and oversee testing.
 Policy makers and the public must find the balance between privacy concerns and infection control to allow the infection status of most Americans to be accessed and validated in a few required settings and many voluntary ones.
Policy makers and the public must find the balance between privacy concerns and infection control to allow the infection status of most Americans to be accessed and validated in a few required settings and many voluntary ones.

Whenever possible, incentives should be used to nudge the voluntary use of these apps rather than require them.
Create a Covid-19 Data Commons and Digital Platform
Real-time analyses of resource allocations, disease tracing results and patient medical records will enable policy makers and researchers to make best use of available resources to identify the most promising areas for surges in testing volumes to snuff out Covid-19 recurrent outbreaks and identify the most promising therapeutic treatments and algorithms.
ACTION STEPS:

This effort would support recent Department of Health and Human Services Federal and State collaboration with leading edge data technical firms to develop an integrated, real-time data platform so testing levels can be aligned at regional levels with illness burden. This platform can enhance procurement, distribution and deployment of tests as those tests evolve in quantity and function. It should also enable state and local authorities to track testing results and capacities to identify spot shortages. This will help identify any supply and demand constraints so that testing levels can be aligned at regional levels with illness burdens.

When integrated into national and state surveillance systems, such innovations may enable the same level of outbreak detection with fewer tests. Promising techniques include anonymous digital tracking of workforces or population-based resting heart-rate and smart thermometer trends; continually updated epidemiological data modeling; and artificial intelligence projections based on clinical and imaging data.

This requires that such data be aggregated and examined, while anonymizing personal identification, to determine optimal treatment paradigms and give leads for structured clinical trials.
The Way Forward
Recent reports from the American Enterprise Institute[i], Center for American Progress[ii], Duke Margolis Center[iii], Harvard University Safra Center for Ethics[iv], and Johns Hopkins University[v] each provide unique, complementary perspectives toward a comprehensive approach for relaxing social distancing and reopening our communities and our economy.
Monitoring the pandemic and adjusting social distancing measures will require launching the largest public health testing program in American history. Successful implementation of a national plan to fast-track Covid-19 testing should allow the country to reopen and respond to recurrent outbreaks. The effort will ultimately grow to billions of dollars per month although innovations in testing technology should eventually drop costs. But with widespread business closures costing the country $350 billion to $400 billion each month, the expense will be worth it. This testing infrastructure is intended to tide the country over until a vaccine or therapy is widely available.
Coordination of such a massive program should be treated as a wartime effort, with a public/private bipartisan Pandemic Testing Board established to assist and serve as a bridge between local, state, and federal officials with the logistical, investment and political challenges this operation will inevitably face. Harvard’s Edmond J. Safra Center for Ethics has done an excellent job of outlining possible options (Appendix A). We recommend a combination of federal and state appointed members who would actively serve throughout the crisis.
Contributors
The Rockefeller Foundation is grateful to the following people who have contributed to this Action Plan through their participation in the video-conference Roundtable on Fast-Track Testing to Restart the Economy (April 9, 2020), through exchanges following the video-conference, or through other collaborations. Some may differ with aspects of it, or have stressed other matters of primary focus. All have contributed with the greatest sense of shared purpose at this time of national need.
Danielle Allen, PhD
James B. Conant University Professor, and Director of the Edmond J. Safra Center for Ethics
Harvard University
Steven Berry, PhD
David Swenson Professor of Economics, Faculty Director of the Tobin Center for Economic Policy
Yale University
Dr. Caroline Buckee
Associate Professor of Epidemiology, Associate Director of Center for Communicable Disease Dynamics
Harvard University
Dr. Lisa A. Cooper
Bloomberg Distinguished Professor and Director, Johns Hopkins Center for Health Equity
Johns Hopkins University
Zack Cooper, PhD
Associate Professor of Public Health, of Economics, and in the Institution for Social and Policy Studies
Yale University
Dr. Ezekiel J. Emanuel
Vice Provost for Global Initiatives, Professor of Medical Ethics and Health Policy
University of Pennsylvania
Robert Grossman, PhD
Frederick H. Rawson Professor of Medicine, Director of the Center for Data and Intensive Science
University of Chicago
Dr. Margaret Hamburg
Chair of the Board
American Association for the Advancement of Science
Gardiner Harris
Former Medical and Science Senior Correspondent
The New York Times
Zia Khan, PhD
Senior Vice President, Innovation
The Rockefeller Foundation
Dr. Rick Klausner
Chief Executive Officer
Lyell Immunopharma, Inc.
Dr. Mark McClellan, PhD
Director, Duke-Margolis Center for Health Policy
Duke University
Allyala Krishna Nandakumar, PhD
Professor of the Practice; Director, Institute for Global Health and Development; Director, MS Program in Global Health Policy and Management
Brandeis University
Eileen O’Connor, JD
Senior Vice President, Communications, Policy, and Advocacy
The Rockefeller Foundation
Michael Osterholm, PhD, MPH
Director, Center for Infectious Disease Research and Policy
University of Minnesota
Dr. Michael Pellini
Managing Partner of Section 32
Board Member of the Personalized Medicine Coalition
Dr. Jonathan D. Quick
Managing Director, Pandemic Response, Preparedness, and Prevention
The Rockefeller Foundation
Dr. Naveen Rao
Senior Vice President, Precision Public Health
The Rockefeller Foundation
Caitlin Rivers, PhD
Senior Scholar, Assistant Professor
Johns Hopkins Center for Health Security
Paul Romer, PhD
Professor at New York University
2018 Nobel laureate in Economics
Dr. Rajiv J. Shah
President
The Rockefeller Foundation
Dr. Jeremy Sugarman
Professor of Bioethics and Medicine, Berman Institute of Bioethics and School of Medicine
Johns Hopkins University
Andrew Sweet
Special Advisor, Covid-19 Response
The Rockefeller Foundation
Evan Tachovsky
Lead Data Scientist & Director, Data and Technology
The Rockefeller Foundation
Dr. Eric Topol
Executive VP and Chair of Innovative Medicine
Scripps Research Translational Institute
Dr. Nana A. Y. Twum-Danso
Managing Director, Health
The Rockefeller Foundation
Elizabeth Yee
Chief of Staff
The Rockefeller Foundation
- Report
Covid-19 Testing Action Plan
With the first wave of infections from the Covid-19 pandemic cresting in much of the country, American political and business leaders are considering plans to reopen the economy. Our National Covid-19 Testing Action Plan is intended to serve as a resource guide to safely achieve that all-important project.Download PDF - Report
National Covid-19 Testing Action Plan: Executive Summary
As the U.S. considers plans for reopening, how can the country strike a balance between increasing economic activity & lowering Covid-19 infection rates? Testing, testing, testing. Read the Executive Summary for an overview of our new national testing strategy:Download PDF
References
[i] https://www.aei.org/research-products/report/national-coronavirus-response-a-road-map-to-reopening/
[ii] https://www.americanprogress.org/issues/healthcare/news/2020/04/03/482613/national-state-plan-end-coronavirus-crisis/
[iii] https://healthpolicy.duke.edu/sites/default/files/atoms/files/covid-19_surveillance_roadmap_final.pdf
[iv] https://ethics.harvard.edu/files/center-for-ethics/files/white_paper_6_testing_millions_final.pdf
[v] https://www.centerforhealthsecurity.org/our-work/pubs_archive/pubs-pdfs/2020/a-national-plan-to-enable-comprehensive-COVID-19-case-finding-and-contact-tracing-in-the-US.pdf